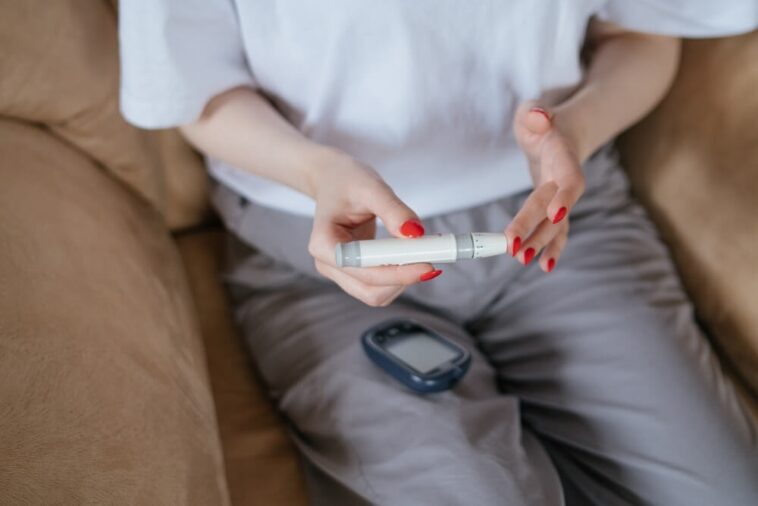
The main source of energy for the mortal body is glucose, a simple sugar. It is a necessary nutrient for the efficient operation of numerous body functions. The role of glucose in the human body will be covered in this article.
1. Energy Production:
Glucose serves as the body’s primary energy source. In a process known as cellular respiration, it is converted into ATP (adenosine triphosphate). The body’s energy unit is ATP, which is necessary for all physiological functions such muscle contraction, digestion, and neuron function.
2. Brain Function:
Glucose serves as the brain’s primary energy source and is strongly reliant on it. Through the blood-brain barrier, glucose is delivered to the brain where it is metabolized to create energy for brain activity. Insufficient glucose can cause lightheadedness, confusion, and fainting. Consistent glucose intake is necessary for healthy brain function.
3. Regulating Blood Sugar:
Blood sugar levels are greatly regulated by glucose. Upon consumption, carbohydrates are converted to glucose and are subsequently absorbed into the bloodstream. The pancreas secretes the hormone insulin to aid in bringing glucose from the bloodstream into cells where it can be used as fuel. By encouraging the storage of glucose in the liver and muscles, insulin also contributes to the lowering of blood sugar levels.
4. Muscle Function:
Muscle function requires glucose. The body utilizes the glycogen (stored glucose) in the muscles as a source of energy during exercise. Additionally, glucose is necessary for the synthesis of ATP, which is necessary for muscular contraction.
5. Red Blood Cell Function:
Red blood cells can only use glucose as an energy source. They lack mitochondria, which are the organelles in which ATP is made. As a result, red blood cells use the process of glycolysis to produce energy from glucose.
6. Maintaining Metabolism:
Additionally, glucose is necessary for the efficient operation of the metabolism. The complicated series of chemical events that take place inside of cells to sustain life are referred to as metabolism. Numerous of these processes, including the synthesis of amino acids, fatty acids, and nucleotides, depend on glucose.
In conclusion, glucose is an important food that is required for human health. It is the body’s principal energy source, necessary for healthy brain function, for controlling blood sugar levels, for the appropriate functioning of muscles and red blood cells, and for regulating metabolism. To guarantee a consistent supply of glucose for the body’s numerous operations, one needs to eat a balanced diet that includes carbohydrates.